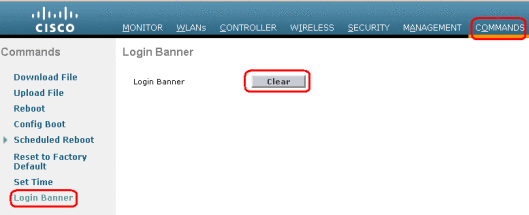
- Cisco Wlc Login Banner
- Cisco Wlc Default Login
- Cisco Wlc Login Portal
- Cisco Wlc Login Email
- Cisco Wlc Login Password
Feb 06, 2013 Here is the way you set up login banner for WLC. First of all you have to create your banner in notepad and save it as a.txt file. Then you have to download this onto WLC using a TFTP server.
Simple and Secure Wireless Deployment and Management for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses and Enterprise Branch Offices.
- Log in to the Cisco WLC Web-Browser interface and go to Advanced Settings. Go to Security - Access Control Lists and add two new ACL rules permitting.
- The video demonstrates the concept of Mobility Anchor for guest users on Cisco Wireless LAN Controller. We will extend our knowledge of mobility tunnel, foreign and anchor controllers, from the.
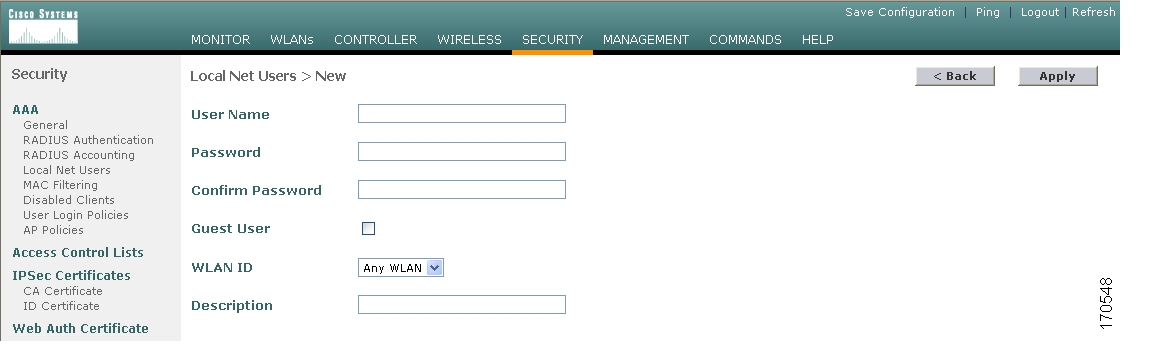
Figure 1. Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The Cisco® Wireless LAN Controller Module allows small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and enterprise branch offices to cost-effectively deploy and manage secure WLANs. The module provides unparalleled security, mobility, and ease of use for business-critical WLANs, delivering the most secure enterprise-class wireless system available. As a Cisco Integrated Services Router module, it delivers centralized security policies, wireless intrusion prevention system (IPS) capabilities, award-winning RF management, quality of service (QoS), and Layer 3 fast secure roaming for WLANs. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module manages up to six Cisco Aironet® lightweight access points and is supported on Cisco 2800/3800 Series integrated services routers and Cisco 3700 Series routers.
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module is a member of the Cisco Wireless LAN controller product family. It works in conjunction with Cisco Aironet lightweight access points, the Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), and the Cisco Wireless Location Appliance to support mission-critical wireless data, voice, and video applications.
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module provides zero-touch access point deployment and configuration, making it easy for IT managers to extend secure wireless networks to branch offices. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module eliminates the need to individually configure, manage, and monitor each access point. In conjunction with Cisco Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP)-enabled access points and the Cisco WCS, the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module minimizes deployment and operational costs, allowing businesses with limited IT staffs to easily deploy and manage wireless networks across hundreds of remote sites.
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module enables enterprises to create and enforce policies that support business-critical applications. From voice and data services to location tracking, the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module provides the manageability and performance that IT managers require to extend their secure enterprise-class 802.11 wireless networks to branch offices (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Converged Wireless and Wired Branch Office with Secure Data, Voice, Switching, and Wireless
Simplified Deployment and Management
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module is easy to deploy and cost-effective to own and operate. It provides maximum flexibility to deploy in SMBs and in enterprise branch offices. It supports zero-touch deployments that do not require manual or pre-configuration of the access points.
When deployed with the Cisco WCS, the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module supports enhanced monitoring and troubleshooting features, including intuitive heat map displays, alarm filtering, event correlation, and granular reporting tools. It also supports template-based configuration management via Cisco WCS Software (optional). These intuitive templates enable the quick application of systemwide security configurations, QoS policies, mobility groups, back-end services, and other configurations via the easy-to-use, award-winning Cisco Unified Wireless Network user interface.
Cisco Wlc Login Banner
Intelligent RF Management
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module is equipped with embedded software for adaptive real-time RF management. The Cisco Unified Wireless Network uses Cisco's patent-pending Radio Resource Management (RRM) algorithms that detect and adapt to changes in the air space in real time. These adjustments create the optimal topology for wireless networking in much the same way that routing protocols compute the best possible topology for IP networks. Cisco RMM creates an intelligent RF control plane for self-configuration, self-healing, and self-optimization of the wireless network (Figure 3).
Cisco RRM algorithms improve wireless LAN operations; tighten wireless security by creating a 'defense shield' that helps prevent unauthorized access from outside the RF domain; and enable businesses to deploy mission-critical wireless applications such as voice.
Figure 3. Enterprise Wide RF Intelligence
Specific intelligent RF capabilities managed by the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module include:- Dynamic Channel Assignment-802.11 channels are adjusted to optimize network coverage and performance based on changing RF conditions.
- Interference Detection and Avoidance-The system detects interference and recalibrates the network to avoid performance problems.
- Load Balancing-The system provides automatic load balancing of users across multiple access points for optimum network performance, even under heavy load.
- Coverage Hole Detection and Correction-RMM software detects coverage holes and attempts to correct them by adjusting the power output of access points.
- Dynamic Power Control-The system dynamically adjusts the power output of individual access points to accommodate changing network conditions, helping to ensure predictable wireless performance and availability.
Enterprise-Class Security
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module for integrated services routers provides the industry's most comprehensive wireless LAN security solution. The module adheres to the strictest level of security standards, including:- 802.11i Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), WPA, and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- 802.1X with multiple Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) types, including Protected EAP (PEAP), EAP with Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS), EAP with Tunneled TLS (EAP-TTLS), and Cisco LEAP
In the Cisco Unified Wireless Network, access points simultaneously act as air monitors and data forwarding devices. This allows access points to communicate real-time information about the wireless domain, including RF noise floor measurements, interference, and potential security threats
to Cisco Wireless LAN controllers, without interrupting service. All security threats are rapidly identified and presented to network administrators via the Cisco WCS, where accurate analysis can take place and corrective action can be taken.

Cisco Systems® provides the only wireless LAN system that offers simultaneous wireless protection and wireless LAN service delivery. This
helps to ensure complete wireless LAN protection, with no unnecessary overlay equipment costs or extra monitoring devices. The Cisco Unified Wireless Network can be deployed initially as a standalone wireless IPS, and reconfigured later to add wireless LAN data service. This allows network managers to create a 'defense shield' around their RF domains, containing unauthorized wireless activity until an organization is ready
to deploy wireless LAN services.
Cisco addresses wireless LAN security by offering multiple layers of protection (Figure 4), including:

- RF Security-Detects and avoids 802.11 interference, and controls unwanted RF propagation.
- Wireless LAN Intrusion Prevention and Location-Detects and locates rogue devices or potential wireless threats, helping IT administrators to quickly assess the threat level and take immediate action to mitigate threats as required.
- Identity-Based Networking-Enables enterprises to deliver individualized security policies to wireless users or groups of users with different access rights, device formats, and application requirements. The security policies include:
- Layer 2 security: 802.1X (PEAP, LEAP, TTLS), WPA, 802.11i (WPA2)
- Layer 3 (and above) security: IP Security (using VPN pass through), Web authentication
- VLAN assignments
- Access control lists (ACLs): IP restrictions, protocol types, ports, and differentiated services code point (DSCP) values
- QoS: Multiple service levels, bandwidth contracts, traffic shaping, and RF utilization
- Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA)/RADIUS: User session policies and rights management
- Network Admission Control (NAC)-Enforces policies pertaining to client configuration and behavior, to help ensure that only end-user devices with appropriate security utilities can gain access to the network.
- Secure Mobility-Maintains the highest level of security in mobile environments with Cisco Proactive Key Caching (PKC), an extension to the 802.11i standard and precursor to the 802.11r standard that facilitates secure roaming with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption and RADIUS authentication.
- Guest Tunneling-Allows enterprises to provide guest access for users without sacrificing security for their corporate networks. Guest tunnels place all guest traffic into tunnels that terminate outside of a company's firewall. Guest switch tunneling can be initiated on the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module, but cannot be terminated. For terminating guest switch tunneling, a Cisco 44xx Wireless LAN Controller is required.
Figure 4. Multiple Layers of Wireless LAN Protection
Real-Time Application Support
The Cisco Unified Wireless Network provides best-in-class performance to support real-time applications such as voice. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module enables rapid handoff between access points, providing mobility to the client. Intelligent queuing and contention management schemes provide effective resource management of the air space, helping to ensure that voice and data traffic are reliably serviced out of a single wireless network. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module also supports QoS capabilities that are Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM)-compliant and closely mirror the emerging IEEE 802.11e standard. Full compliance with the finished standard will be achieved via a software upgrade when the final standard is ratified.
Mobility
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module for integrated services routers allows users to roam between access points and across bridged and routed subnets without requiring changes to the underlying infrastructure. Security and QoS context information follows users wherever they roam, helping to ensure that mobility does not compromise performance, reliability, or privacy. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module does not require client devices to load any special software to enable mobility (Mobile IP clients, for example).
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Cisco Wlc Default Login
Table 1. Features and Benefits of the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module
Feature | Benefits |
| Integrated Into Cisco Routers | |
| Zero-touch Configuration | The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module eliminates the need to individually configure, manage, and monitor each access point. It provides zero-touch LWAPP-enabled access point configuration and is ideal for environments with limited onsite IT support, such as branch offices within a distributed enterprise. By managing all access points as a complete wireless LAN system, the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module provides complete wireless LAN control and maximizes wireless LAN performance. |
| Centralize Management Across Many Branches | A single Cisco WCS can manage 100 wireless LAN controller modules located across several remote sites. The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module can also be managed without a Cisco WCS, using a CLI or an intuitive Web interface. |
| RF Security | Integrated wireless intrusion prevention preserves the integrity of wireless networks |
| Integrated RRM | The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module creates an intelligent RF control plane for self-configuration, self-healing, and self-optimization. |
| Fast Secure Mobility | Fast secure roaming between access points enables low-latency applications such as |
SUMMARY
Cisco Wlc Login Portal
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module provides network administrators with the visibility and control they need to effectively manage enterprise-class wireless LANs at remote sites. With the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module, SMBs and enterprise branch offices can cost-effectively support their network requirements with converged networks that integrate data, voice, video, and wireless.
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module provides zero-touch access point configuration and is ideal for environments with limited onsite IT support, such as branch offices within a distributed enterprise. In conjunction with Cisco Aironet lightweight access points and the Cisco WCS, the Wireless LAN Controller Module reduces deployment and operational costs of deploying and managing wireless LANs.
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2. Product Specifications for the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module
Cisco Wlc Login Email
Item | Specification |
| Wireless | Access points supporting IEEE 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11d, and 802.11h |
| Wired/Switching | Several Ethernet switching modules and PoE options are supported on Cisco 2800, 3700, and 3800 series routers |
| Data Rfcs | |
| Security Standards | |
| Encryption | |
| AAA | |
| Management | |
| Management Interfaces | |
| Physical and Environmental | |
| Regulatory Compliance | |
| Product Compatibility | |
| Software Compatibility | Routers: Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.4(third release)T and later |
Cisco Wlc Login Password
ORDERING INFORMATION
Table 3. Ordering Information for the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module
Part Number | Product Name |
NM-AIR-WLC6-K9 | Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module for managing up to 6 lightweight access points (when sold as part of ISR system) |
NM-AIR-WLC6-K9= | Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module for up to 6 lightweight access points (spare, ordered as an individual unit) |